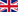
Synergies of Bionic µFuel & µSoil
Bionic µFuel and µSoil combine climate protection, energy efficiency, and circular economy in an integrated system. Industrial residues and organic materials are converted into energy, high-quality carbon products, and stable fertilizers – with clearly measurable climate impact and additional revenue potential, including through CO₂ removal.
At the same time, µFuel and µSoil reduce NH₃ and N₂O emissions in agriculture and support key objectives of the EU Green Deal, the Circular Economy, and security of supply in energy and fertilizers. The technologies create measurable synergies between industry, agriculture, policy, research, and mechanical engineering.
CO₂ Sink
Permanent CO₂ removal through biochar/µSoil with certifiable carbon removal credits.
NH₃ & N₂O Saving
Low-emission fertilizer systems that significantly reduce ammonia and nitrous oxide emissions.
Energy & Storage
Pyrolysis oil, gas, and char as flexible energy source and component for power-to-oil concepts.
Industry & Licenses
Building new mechanical engineering ecosystems with local manufacturing and export potential.
At a Glance: Where Bionic µFuel & µSoil Create Synergies
Bionic technologies unfold their impact across numerous economic, research, and policy fields. Use the following overview to navigate directly to the respective sectors.
| Sector | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Agriculture (Arable & Grassland) | Stable µSoil fertilizer systems, soil building, resilient yields |
| Livestock Farms & Manure Utilization | Conversion of manure into storable fertilizer, reduced storage and emission pressure |
| Forestry & Reforestation Projects | Regeneration of degraded areas with µSoil and long-term carbon sequestration |
| Industry & Commerce with Residues | Utilization of production residues for own energy and process heat |
| Wood, Agricultural & Food Industry | Conversion of biogenic by-products into energy, oil, and carbon |
| Paper, Pulp & Packaging Industry | Residue utilization, process heat, reduction of disposal costs |
| Tire Industry & Tire Recyclers | Production of black carbon and high-quality oil fractions |
| Plastic Recycling & Sorting Plants | Thermal decomposition of mixed plastics into oil and carbon |
| Composites, Wind Power & White Goods | Processing of complex composites and recovery of metals & fibers |
| Municipalities & Municipal Waste Management | Regional circular economy, local energy and residue utilization |
| Water Utilities & Drinking Water Suppliers | Activated carbon filters from biochar for removal of pharmaceutical and pollutant residues |
| Wastewater Treatment Plants & Water Associations | Regenerable filter and adsorption systems, integration with energy generation |
| Utilities & Energy Suppliers | Low-carbon substitute fuels, power-to-oil approaches, and storage options |
| Decentralized Grid & District Operators | Integrated district solutions with local fuel production |
| Offshore & Island Locations | Reduction of fuel transport through local oil and gas production |
| Remote Sites in Resource Projects | Supply of remote camps with on-site generated energy |
| ETS-Obligated Companies | Optimization of CO₂ costs, certificate portfolios, and CDR strategies |
| Investors, Banks & Funds | ESG & impact investments with physical asset base and CDR revenues |
| Policy, Ministries & Funding Agencies | Design of programs for CO₂ sinks, circular economy, and fertilizer security |
| Research Institutions & Universities | Lab reactors for material testing, specialty biochars, and microwave research |
| High-Tech Industry & Supercapacitors | Development of electrode materials, graphene-like structures, and functional carbons |
| Mechanical Engineering Companies & Licensees | Building national manufacturing, service ecosystems, and local value creation |
CO₂ Sink with Clear Business Case
Bionic µFuel and µSoil create a scalable CO₂ sink: carbon is permanently sequestered in the form of biochar in soil or in technical applications. Per ton of biochar produced, a measurable and certifiable carbon removal performance is generated.
The combination of CO₂ reduction and CO₂ removal is decisive: fossil fuels are replaced, while at the same time additional CO₂ is permanently removed from the cycle. This creates attractive revenue models – such as through the sale of biochar carbon removal credits – and a significant improvement in the climate balance.
Key Revenue Sources
- Savings through CO₂ saving (energy, process heat, efficiency)
- Revenue from CO₂ removal credits (biochar CDR, carbon removal certificates)
- Reduction of disposal, storage, and transport costs
- Product sales: oil, gas, carbon products, specialty biochar
- Value creation through mechanical engineering, service, operation, and licensing systems
NH₃ & N₂O Saving in Agriculture
With µSoil, animal excreta are no longer applied to fields as manure in the traditional way, but processed with biochar into a stable, storable fertilizer system. This significantly reduces ammonia (NH₃) and nitrous oxide (N₂O) emissions.
Nutrients are better bound, released more slowly, and distributed more evenly. In addition to the climate impact, soil structure, water storage capacity, and field resistance to erosion and drought stress improve.
Climate Impact & Environmental Benefits
- Significant reduction of NH₃ emissions by avoiding open manure application
- Reduction of N₂O emissions through controlled nitrogen release
- Less methane formation through shorter and smaller manure storage
- Protection of groundwater and surface water through reduced nitrate leaching
- Homogeneous, plant-compatible fertilization instead of point overload
Agriculture (Arable & Grassland)
Soil health, stable yields, and low-emission fertilization with µSoil.
µSoil combines several requirements of modern agriculture: higher soil health, stable yields, reduced dependence on mineral fertilizers, and lower emissions. The combination of biochar with nutrient fractions from excreta creates an easily manageable, homogeneously applicable fertilizer.
Structurally stable biochar improves water retention and air exchange in the soil, microorganisms find permanent habitats, and nutrients are bound long-term. As a result, yield security and resilience increase while mineral fertilizer use decreases.
For arable and grassland areas, this means: improved water availability during dry periods, higher biological activity in the soil, and more uniform nutrient supply to plants throughout the growing season.
Benefits Overview
Agronomic Effects
- Soil structure improvement and humus buildup
- Higher water storage capacity
- Better nutrient availability for plants
- Reduced mineral fertilizer input
Climate Impact
- CO₂ sink through permanent carbon sequestration
- NH₃ and N₂O reduction
- Less nitrate leaching into groundwater
Farm Economics
- More stable yields and higher resilience
- Better predictability of fertilizer applications
- Optional additional revenue from biochar/µSoil products
Livestock Farms & Manure Utilization
Conversion of manure into storable fertilizer with reduced emissions.
For farms with intensive livestock production, µSoil offers a solution for manure management: Through the conversion of manure and barn fractions into µSoil, requirements for manure storage capacity decrease significantly, odor emissions decline, and application can be better adapted to weather and plant needs.
Nutrients are better bound, released more slowly, and distributed more evenly. In addition to the climate impact, soil structure, water storage capacity, and field resistance to erosion and drought stress improve.
The storable µSoil fertilizer can be applied as needed, independent of closed periods or unfavorable soil conditions. This increases operational flexibility and reduces the risk of nutrient losses due to unfavorable application conditions.
Benefits Overview
Manure Management
- Lower storage and application costs
- Reduction of odor emissions
- More flexible application timing
- Less storage and emission pressure
Climate Impact
- Significant NH₃ emission reduction
- Reduction of N₂O emissions
- Less methane formation in manure storage
Operational Advantages
- Homogeneous nutrient distribution
- Better predictability of fertilization
- Independence from closed periods
Forestry & Reforestation Projects
Regeneration of degraded areas with µSoil and long-term carbon sequestration.
In forestry and reforestation projects, µSoil offers an effective method for regenerating degraded soils. Through the incorporation of biochar, water retention, nutrient availability, and biological activity improve even on heavily damaged sites.
Young plants benefit from improved soil structure and more stable water supply, leading to higher establishment rates and faster juvenile growth. Long-term carbon sequestration in the soil complements CO₂ storage by the growing forest stand.
For large-scale reforestation projects, combined climate protection effects emerge: aboveground biomass stores CO₂, while at the same time stable carbon is permanently deposited in the soil. This creates synergies between traditional forestry and innovative carbon sinks.
Benefits Overview
Soil Regeneration
- Improvement of degraded sites
- Increased water retention capacity
- Promotion of soil biology
- Better nutrient availability
Reforestation Success
- Higher establishment rates of young plants
- Faster juvenile growth
- Better drought resilience
Climate Impact
- Combined CO₂ storage (biomass + soil)
- Long-term carbon sequestration
- Certifiable carbon removal performance
Industry & Commerce with Residues
Decarbonization with own residues and predictable energy.
Many industries have continuous residue streams from their production processes. With µFuel, these material streams can be converted directly on-site into energy, oil, gas, and biocarbon – an efficient form of utilization instead of costly disposal.
This covers part of the energy and process heat supply from own resources. Companies reduce their CO₂ footprint, become more independent of global energy price fluctuations, and simultaneously reduce disposal and logistics costs.
Particularly attractive is the coupling with CO₂ strategies: µFuel plants can be integrated into decarbonization roadmaps, ESG strategies, and net-zero plans. The biochar produced offers additional revenue potential through carbon removal credits and specialty applications.
Benefits Overview
Typical Applications
- Industrial production residues
- Organic by-products
- Process waste and rejects
- Packaging materials
Technical Synergies
- Integration into process heat and steam systems
- Utilization instead of disposal
- Combination with waste heat recovery and ORC systems
Economic Effects
- CO₂ saving and certificate benefits
- Reduced disposal and transport costs
- Savings on fossil fuels
- Additional revenue from biochar and oil products
Wood, Agricultural & Food Industry
Conversion of biogenic by-products into energy, oil, and carbon.
The wood, agricultural, and food industries generate large quantities of biogenic by-products: wood residues, sawdust, pomace, shells, kernels, and plant production waste. µFuel enables the conversion of these materials into valuable energy carriers and carbon products.
Instead of disposal costs, revenues are generated through energy production and product sales. Companies can partially cover their process heat supply from own residues and simultaneously reduce CO₂ emissions.
The biochar produced finds buyers in agriculture, the environmental sector, or as raw material for specialty applications. This creates a regional circular economy with clearly measurable value creation.
Benefits Overview
Typical Materials
- Wood residues and sawdust
- Pomace, shells, kernels
- Plant production waste
- Organic by-products
Energy Use
- Process heat and steam generation
- Pyrolysis oil as fuel
- Process gas for CHP applications
Economic Effects
- Disposal costs become revenues
- Self-supply with process heat
- Sale of biochar and oil
- CO₂ reduction and climate protection
Paper, Pulp & Packaging Industry
Residue utilization, process heat, and reduction of disposal costs.
The paper, pulp, and packaging industries produce large quantities of residues: bark, wood fibers, waste paper rejects, sludge, and packaging waste. µFuel converts these materials into process heat, steam, and biocarbon.
Particularly interesting is the possibility of partially supplying energy-intensive processes such as drying and steam generation with own residues. This reduces the need for purchased energy and lowers production costs.
The biochar produced can be used as filler, filter material, or in special product applications. At the same time, disposal costs and transport efforts for residues decrease.
Benefits Overview
Typical Residues
- Bark and wood fibers
- Waste paper rejects
- Production sludge
- Packaging waste
Process Integration
- Steam generation for drying
- Process heat for production steps
- Reduction of purchased energy
Economic Benefits
- Reduction of disposal costs
- Reduction of energy costs
- Additional revenue through biochar
- CO₂ footprint improvement
Tire Industry & Tire Recyclers
Production of black carbon and high-quality oil fractions.
End-of-life tires are a challenging recycling material: the combination of rubber, steel, and textiles is mechanically difficult to separate. µFuel opens new pathways: tires are thermally decomposed and separated into high-quality fractions.
The resulting black carbon is a sought-after material for the rubber and plastics industry. Oil fractions can serve as fuel or raw material for the chemical industry. Metals and fibers are recovered in pure form and can be fed back into the cycle.
For tire manufacturers and recyclers, new business models emerge: instead of disposal costs, high-quality secondary raw materials are produced that can flow back into production processes.
Benefits Overview
Product Fractions
- Black carbon (recovered carbon black - rCB)
- High-quality oil fractions
- Process gas
- Steel cord and textiles (pure)
Market Opportunities
- Sale of rCB to rubber/plastics industry
- Oil as fuel or chemical feedstock
- Recovery of metals
Economic Effects
- High product values instead of disposal costs
- New business models in tire recycling
- Contribution to circular economy
Plastic Recycling & Sorting Plants
Thermal decomposition of mixed plastics into oil and carbon.
Plastic recycling reaches limits with mixed or contaminated fractions. Sorting plants produce residues that are no longer mechanically recyclable. µFuel offers a thermal solution: mixed plastics are decomposed into pyrolytic oil, gas, and carbon.
The pyrolysis oil can be used as chemical feedstock in plastic production – a true circular closure. Energy-rich process gas can be used for energy supply, while carbon finds use as filler or adsorption material.
For sorting plants and recycling operations, a solution emerges for previously difficult-to-recycle fractions. Instead of incineration or landfilling, a higher-value recovery path is opened.
Benefits Overview
Input Materials
- Mixed plastic fractions
- Sorting residues and rejects
- Contaminated plastics
- Multi-layer packaging
Products
- Pyrolysis oil (chemical feedstock)
- Process gas (energy)
- Carbon (filler, adsorber)
- Recovered metals
Advantages
- Higher-value recovery vs. incineration
- Circular closure through oil-to-plastic
- Reduction of landfill volumes
Composites, Wind Power & White Goods
Processing of complex composites and recovery of metals & fibers.
Composite materials such as GRP, CFRP, wind turbine blades, or electronic waste are mechanically difficult to separate. µFuel enables thermal decomposition of these complex materials: plastic matrices are decomposed, metals and fibers remain and can be separated in pure form.
Wind turbine blades generate large amounts of GRP and CFRP waste, whose disposal is problematic. Through µFuel, the fibers are exposed and can be recycled. The plastic matrix becomes oil, gas, and carbon.
For white goods (refrigerators, washing machines) and electronic waste, metals, plastics, and foams can be thermally decomposed in one step. This simplifies recycling and increases recovery rates.
Benefits Overview
Application Areas
- Wind turbine blades (GRP/CFRP)
- Composite components from aerospace/automotive
- Electronic waste and circuit boards
- White goods (refrigerators, washing machines)
Recovery Products
- Glass and carbon fibers (reusable)
- Pure metals (Cu, Al, Fe)
- Pyrolysis oil and gas
- Carbon residues
Advantages
- Solution for difficult-to-separate composites
- High recovery rates
- Avoidance of landfilling
Municipalities & Municipal Waste Management
Regional circular economy and local climate strategies.
Cities and municipalities face the task of reducing waste streams, providing energy locally, and meeting climate targets. µFuel plants can be deployed at recycling centers, waste management facilities, or municipal infrastructure sites to locally utilize green waste, wood residues, bulky waste fractions, and selected residues.
Previously cost-intensive waste streams become energy, pyrolytic fuels, and biocarbon. Municipal climate strategies can demonstrate concrete CO₂ savings while simultaneously creating regional value creation. For districts and municipal associations, joint plant clusters are an option.
The combination with municipal heat or district heating networks, wastewater treatment plants, or landfill sites enables integrated solutions with high visibility for citizens.
Benefits Overview
Typical Applications
- Municipal waste management centers
- Recycling and construction yards
- Regional climate and energy agencies
Technical Synergies
- Coupling with district heating networks
- Integration into existing infrastructure
- Use of local residue potentials
Economic Effects
- Lower transport and disposal costs
- Local energy generation with CO₂ saving
- Support for municipal funding projects
Water Utilities & Drinking Water Suppliers
Activated carbon filters from biochar for removal of pharmaceutical and pollutant residues.
Biochar can be refined into high-performance activated carbon. Water utilities can use this as filter material to remove dissolved organic substances, pharmaceutical residues, hormones, and trace substances from drinking water.
A key advantage is regenerability: through renewed thermal treatment, filter materials loaded with pollutants can be returned to a usable state. This creates a circular filter system that conserves resources and reduces waste volumes.
Biochar activated carbon can be tailored to specific requirements: pore size, surface structure, and adsorption properties can be specifically adjusted through the pyrolysis process.
Benefits Overview
Applications
- Drinking water utilities
- Municipal water suppliers
- Industrial process water treatment
Filter Performance
- Removal of pharmaceuticals and hormones
- Adsorption of trace substances
- Reduction of heavy metals
- Removal of dissolved organic substances
Advantages
- Regenerable filter materials
- Tailored activated carbon properties
- Contribution to drinking water protection
Wastewater Treatment Plants & Water Associations
Regenerable filter and adsorption systems, integration with energy generation.
Wastewater treatment plants produce large quantities of sewage sludge, whose disposal is increasingly problematic. µFuel converts sewage sludge into energy, gas, and biochar. The biochar can be used as activated carbon in the fourth treatment stage.
This creates an integrated system: sewage sludge is refined into filter carbon, which in turn removes trace substances and micropollutants from wastewater. At the same time, energy is generated for plant operation.
For water associations and treatment plant operators, this means: a disposal problem becomes a circular system with measurable environmental and cost benefits.
Benefits Overview
Applications
- Municipal and industrial treatment plants
- Water associations and wastewater associations
- Fourth treatment stage
Integrated Solution
- Sewage sludge utilization to activated carbon
- Trace substance removal through biochar filters
- Energy generation from sewage sludge
- Regenerable filter systems
Advantages
- Solution for sewage sludge disposal
- Own energy and filter material production
- Contribution to water protection
Utilities & Energy Suppliers
Low-carbon substitute fuels, power-to-oil approaches, and storage options.
For utilities and energy suppliers, µFuel offers the possibility of converting biogenic residues into low-carbon substitute fuels. Pyrolysis oil can be used in boilers, engines, or turbines, process gas in CHP structures or process heat applications.
Another component is the use of excess electricity: during times of high renewable energy feed-in, energy can be "buffered" in pyrolysis oil and later reconverted during high demand. This creates power-to-oil and storage strategies that can be integrated into existing power plant and grid infrastructures.
In combination with biochar production, a classic energy project becomes a CO₂-negative system that serves energy and climate goals simultaneously.
Benefits Overview
Typical Applications
- Utilities and regional energy suppliers
- Industrial energy service providers
- Combined heat and power plants
Technical Synergies
- Substitute fuels for existing boiler/engine fleets
- Power-to-oil with reconversion
- Combination with heating networks, ORC, and storage technologies
Economic Effects
- Reduction of fossil fuel purchases
- New storage options for fluctuating renewables
- CO₂ reduction and access to CDR markets
Decentralized Grid & District Operators
Integrated district solutions with local fuel production.
District projects and decentralized energy systems benefit from µFuel through local fuel production from green waste, wood residues, and organic residues. The pyrolysis products can be directly fed into district CHP units, heating centers, or decentralized CHP plants.
This creates resilient, locally anchored energy systems with high supply security. At the same time, dependence on district heating or central gas networks is reduced.
In combination with photovoltaics, battery storage, and intelligent control systems, energy-autonomous districts emerge that make a significant contribution to local climate protection goals.
Benefits Overview
Applications
- District energy centers
- Decentralized district heating networks
- Housing cooperatives with self-supply
- Commercial and industrial parks
Integration
- Coupling with PV, storage, and heat pumps
- Local fuel production from residues
- Intelligent energy control
Advantages
- High supply security
- Reduced dependence on district heating/gas
- Contribution to local climate protection goals
Offshore & Island Locations
Reduction of fuel transport through local oil and gas production.
In island regions and offshore installations, fuel transport causes high costs and risks. µFuel allows organic residues, wood, or suitable local materials to be converted into pyrolysis oil and gas, thus covering part of the on-site energy supply.
This improves supply security, reduces dependencies, and lowers the CO₂ balance of the energy used. At the same time, residues can be utilized that would otherwise remain unused or require costly disposal.
For islands with limited access to mainland infrastructure, µFuel offers a decentralized, reliable energy source that uses local resources and minimizes transport efforts.
Benefits Overview
Typical Applications
- Islands and remote regions
- Offshore platforms and wind farms
- Research stations in remote areas
Technical Synergies
- On-site fuel production
- Use of local residues
- Coupling with diesel/hybrid units
Economic Effects
- Reduction of transport and logistics costs
- Less risk from supply chain disruptions
- Improved CO₂ balance of energy supply
Remote Sites in Resource Projects
Supply of remote camps with on-site generated energy.
Resource projects in remote regions – such as mines, drilling sites, or exploration camps – require reliable energy supply under difficult logistical conditions. µFuel enables the use of local organic materials for energy generation.
Wood, plant residues, or organic waste from supply can be converted into pyrolysis oil and gas. This reduces the need for diesel fuel, which often must be transported over long distances and at high costs.
For project operators, this means: cost reduction, higher supply security, and improved environmental balance. At the same time, local resources are used that would otherwise remain unused.
Benefits Overview
Typical Applications
- Mines and mining projects
- Exploration camps and drilling sites
- Infrastructure projects in remote regions
Energy Supply
- Local oil and gas production
- Reduction of diesel transport
- Use of locally available biomass
Advantages
- Reduction of energy costs
- Higher supply security
- Improved environmental and climate balance
ETS-Obligated Companies
Optimization of CO₂ costs, certificate portfolios, and CDR strategies.
Companies subject to the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) face rising CO₂ costs. µFuel offers a way to reduce CO₂ emissions while simultaneously permanently removing CO₂ from the atmosphere.
By converting own residues into energy, fossil fuels are replaced – this reduces ETS-relevant emissions. The biochar produced simultaneously binds CO₂ long-term and creates additional carbon removal performance.
For ETS-obligated operations, several advantages emerge: reduction of certificate costs, building own CDR capacities, and improvement of decarbonization strategies. This positions companies early for tightened climate targets.
Benefits Overview
Climate Impact
- Reduction of ETS-relevant CO₂ emissions
- Additional carbon removal performance
- Building own CDR capacities
Economic Effects
- Reduction of certificate costs
- Improvement of decarbonization strategy
- Early positioning for net zero
Strategic Advantages
- Meeting tightened climate targets
- Improvement of ESG performance
- Competitive advantage through CDR competence
Investors, Banks & Funds
ESG & impact investments with physical asset base and CDR revenues.
µFuel and µSoil projects combine infrastructure character with scalability and clear climate impacts. They are suitable for ESG and impact funds, infrastructure investors, and long-term oriented capital providers who want to map CO₂ reduction and CO₂ removal in their portfolios.
Revenue streams result from energy sales, fuel substitution, disposal savings, product sales (oils, carbon, fertilizers), and carbon removal credits. The modular technology allows project sizes from pilot plants to large cluster projects with many reactors.
For investors, diversified portfolios with measurable climate impacts, stable cash flows, and long-term value creation potentials emerge.
Benefits Overview
Investment Arguments
- Clearly defined physical assets (plants, clusters)
- Predictable revenue path combinations (energy, CDR, products)
- High relevance for ESG and impact strategies
Risk Diversification
- Broad distribution across sectors (industry, agriculture, municipalities)
- Regional cluster strategies and cross-border projects
Scaling
- From single site to international portfolio
- Combination with government funding programs possible
Policy, Ministries & Funding Agencies
Design of programs for CO₂ sinks, circular economy, and fertilizer security.
For policy, ministries, and funding agencies, µFuel and µSoil offer the opportunity to address multiple strategic goals simultaneously: climate protection and CO₂ removal, reduction of NH₃ and N₂O emissions, securing fertilizer supply, waste avoidance, and strengthening regional value creation in industry and agriculture.
The technologies can be embedded in climate protection laws, ETS developments, agricultural and fertilizer strategies, and circular economy programs. Through clear measurability of material flows and emission effects, µFuel and µSoil projects are suitable as reference and flagship projects for national and European initiatives.
Benefits Overview
Action Fields
- Climate protection and CDR strategies (net zero, carbon removal)
- Agricultural and fertilizer policy (NH₃/N₂O reduction, supply security)
- Circular economy and waste strategies
Program Design
- Funding programs for CO₂ sinks and µSoil demonstration projects
- Cluster and regional concepts for industry & agriculture
- Standardization of monitoring, reporting & verification (MRV)
Research Institutions & Universities
Lab reactors for material testing, specialty biochars, and microwave research.
µFuel reactors are not only production plants but also research platforms. Universities and institutes can vary temperature profiles, atmospheres, residence times, and feedstocks to specifically produce specialty biochars with certain properties.
Research focuses include: material and surface development, adsorption properties, microwave interactions with various materials, and optimization of pyrolysis processes for different feedstocks.
For research institutions, µFuel lab reactors offer the opportunity to combine basic research with application-oriented development and to explore new carbon materials for future technologies.
Benefits Overview
Research Fields
- Material and surface development
- Microwave research and process optimization
- Adsorption properties and filter materials
- Feedstock characterization
Lab Reactors
- Flexible parameter adjustment
- Reproducible test conditions
- Fast material screening tests
Perspectives
- Development of specialty biochars
- Transfer to industrial applications
- Publications and patents
High-Tech Industry & Supercapacitors
Development of electrode materials, graphene-like structures, and functional carbons.
Through targeted process control, µFuel reactors can produce carbon materials with exceptional properties: extremely high surfaces, graphene-like structures, conductive or magnetizable carbons.
These materials are interesting for supercapacitors, energy storage systems, electrodes, RF shielding, sensors, and catalytic applications. Through microwave technology, functional carbons with defined properties can be produced.
For the high-tech industry, new possibilities emerge to develop carbon materials from renewable raw material sources – an important step toward sustainable materials economy in high-technology applications.
Benefits Overview
Material Properties
- Extremely high surfaces (>2000 m²/g)
- Graphene-like and conductive structures
- Magnetizable carbons
- Defined pore size distributions
Application Fields
- Supercapacitors and energy storage
- Electrode materials for batteries
- RF shielding and EMC applications
- Sensors and catalysis
Strategic Effects
- Building high-technology know-how
- Linking climate protection and innovation
- Basis for new industrial sites
Mechanical Engineering Companies & Licensees
Building national manufacturing, service ecosystems, and local value creation.
Through licensing models in mechanical engineering, domestic and foreign partners can build their own µFuel and µSoil manufacturing facilities. This creates an independent climate-positive industry in each country that becomes a licensee, with engineering, manufacturing, service, and project development.
These licensing partnerships create high-quality jobs, anchor technologies locally, and open export opportunities to neighboring markets. For industrial policy and economic development, levers emerge with which climate protection and industrial development can be advanced together.
Mechanical engineering companies benefit from a growing market for climate technologies with long-term perspectives in service, maintenance, and plant modernization.
Benefits Overview
Industry Building
- Own national manufacturing and service capacities
- Building engineering and project teams
- Integration with local supply chains
Economy & Employment
- Creation of high-quality industrial jobs
- Export potential in growing CDR and circular markets
Strategic Effects
- Strengthening local value creation
- Technology sovereignty in key areas
- Sustainable contribution to national climate goals
Leverage Synergies – Reduce CO₂ – Increase Value Creation
Bionic µFuel and µSoil combine CO₂ saving, NH₃/N₂O reduction, circular economy, energy supply, and material innovation in one system. The technologies are scalable, economically attractive, and create clear synergies between industry, agriculture, policy, research, and mechanical engineering.
Together with our partners, we develop customized cluster and project solutions – from material flow analysis through CO₂ and NH₃/N₂O balancing to business model and implementation.